
Magnetorheological fluids are another class of non-Newtonian fluids.The viscosity of non-Newtonian fluids, on the other hand, is not constant but varies widely depending on the force applied.Non-Newtonian fluids are what they’re termed. But the viscosity of most fluids varies with the rate of shear.However, water and honey are among the rare examples of fluids that have such a characteristic behavior. Inventor Isaac Newton believed that a fluid’s viscosity would remain constant independent of variations in the shear rate at a certain temperature and shear stress.A Newtonian fluid, on the other hand, behaves as a fluid regardless of how much force is applied to it. Resistance increases as forces are increased, but it’s always proportional. In general, Newtonian fluids have a fixed viscosity.

What viscosity water air oil definition meaning unit kinematic formula equation Newtonian Vs Non-Newtonian Fluids differences We have already learned the other formula of viscosity,
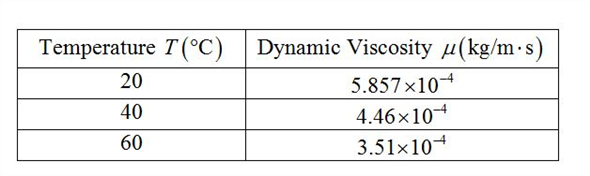
The viscosity of a Newtonian fluid is linearly proportional to the shear stress in a one-dimensional flow. The Reynolds number, which connects the fluid’s momentum to its viscous forces, is one formulation that makes use of kinematic viscosity.

The kinematic viscosity ν=μ/ρ seems often in fluid mechanics and warmth switch and is associated with flows below the pressure of gravity. When managing surprise waves and phenomena that consist of excessive and fast compression of the fluid, the majority viscosity η can’t be neglected, being associated with essential principles together with sound attenuation. Viscosity example boundary layer Kinematic Viscosity In totality, we can say there are three types of viscosity, However, relying on waft physics distinctive viscosities play corresponding essential roles. The maximum usually used withinside the area of fluid dynamics is shear or dynamic viscosity. Poisesulle’s Law is the name given to this concept today, and it is employed in a variety of formulas and equations. For example, he discovered from this experiment that a liquid’s velocity depends on viscosity, provided that the tube’s length and diameter are constant.John-Louis-Marie Poiseuille discovered viscosity in 1829 by testing the flow of liquids through a variety of thin tubes of varying sizes and shapes.John-Louis-Marie Poiseuille and Gotthilf Hagen were the three men who molded viscosity into what it is today.Each of these experts discovered principles that have been combined to aid scientists today build new experiments and calculations.

The discovery of viscosity is remarkable in that it was made three times independently by three distinct scientists, which makes it particularly interesting.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
